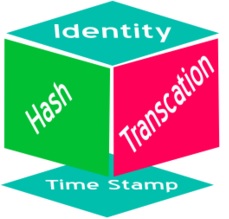
What is Blockchain?
A Blockchain (or block chain) is a method of storing a list of entries, which cannot be changed easily after they are created. This also applies to the list. This is done by using several concepts from cryptography, including digital signatures and hash functions. In very basic terms, a blockchain combines the following two ideas:
1. Given some data, it is easy to calculate a checksum over the data. Special hash functions can be designed to calculate this checksum. These functions can be designed to return a value that always has the same length, which is not dependent on the length of the input. This value is called hash value, or message digest. The functions also have another property: Given the same input, they must return the same output (hash value/message digest).
2. In addition to the hash values, a block typically also contains a timestamp, and some payload. Each block uses a digital signature, which allows detecting any change in the data since the signature was made. When new blocks of data are created, the newly created block will also contain the hash value of the previous block
In most cases, a blockchain is managed by a peer-to-peer network. All peers use a common protocol that specifies how they should communicate with each other, how a new block is created and validated. Once recorded, the data in any given block cannot be changed easily any more. Changing the block means all the blocks after it need to be changed as well. Depending on the protocol, this will require a majority of the peers, or even all the peers, to agree.
Blockchains are secure by design. Blockchain technology is used where keeping a correct record is important. Use cases include medical records, identity management, food traceability, and voting.
Blockchain was invented by Stuart Haber and Scott Stornetta in 1991 as a means to assure the integrity of digital records. Haber and Stornetta launched the world’s first commercial blockchain.
What is a digital wallet?
A digital wallet (or e-wallet) is a software-based system that securely stores users’ payment information and passwords for numerous payment methods and websites. By using a digital wallet, users can complete purchases easily and quickly with near-field communications technology. They can also create stronger passwords without worrying about whether they will be able to remember them later.
Digital wallets can be used in conjunction with mobile payment systems, which allow customers to pay for purchases with their smartphones. A digital wallet can also be used to store loyalty card information and digital coupons.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Digital wallets are financial accounts that allow users to store funds, make transactions, and track payment histories by computer.
- These pieces of software may be included in a bank’s mobile app, or as a payments platform like PayPal or Alipay.
- Digital wallets are also the main interface for using cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin.
Digital Wallet Explained
Digital wallets largely eliminate the need to carry a physical wallet by storing all of a consumer’s payment information securely and compactly. Also, digital wallets are a potential boon to companies that collect consumer data. The more companies know about their customers’ purchasing habits, the more effectively they can market to them. The downside for consumers can be a loss of privacy.
Digital wallets allow many in developing nations to participate more fully in the global financial system. Digital wallets allow participants to accept payments for services rendered, as well as receive funds or remittances from friends and family in other nations. Digital wallets do not require a bank account with a physical firm or branch, often allowing those in poorer and rural areas to be served as well and therefore enables a wider financial inclusion.
Cryptocurrencies rely solely on digital wallets to maintain balances and make transactions, for instance with Bitcoin or other digital currencies like MDCx.
What is a Exchange, like MeteorEX.online?
A cryptocurrency exchange, or a digital currency exchange (DCE), is a business that allows customers to trade cryptocurrencies or digital currencies for other assets, such as conventional fiat money or other digital currencies. Exchanges may accept credit card payments, wire transfers or other forms of payment in exchange for digital currencies or cryptocurrencies. A cryptocurrency exchange can be a market maker that typically takes the bid–ask spreads as a transaction commission for is service or, as a matching platform, simply charges fees.
The exchanges can send cryptocurrency to a user’s personal cryptocurrency wallet. Some can convert digital currency balances into anonymous prepaid cards which can be used to withdraw funds from ATMs worldwide while other digital currencies are backed by real-world commodities such as gold.
The creators of digital currencies are often independent of the digital currency exchange that facilitate trading in the currency. In one type of system, digital currency providers (DCP) are businesses that keep and administer accounts for their customers, but generally do not issue digital currency to those customers directly. Customers buy or sell digital currency from digital currency exchanges, who transfer the digital currency into or out of the customer’s DCP account. Some exchanges are subsidiaries of DCP, but many are legally independent businesses. The denomination of funds kept in DCP accounts may be of a real or fictitious currency.
A digital currency exchange can be a brick-and-mortar business or a strictly online business. As a brick-and-mortar business, it exchanges traditional payment methods and digital currencies. As an online business, it exchanges electronically transferred money and digital currencies.
Decentralized exchanges such as MeteorEX.online, Etherdelta, IDEX and HADAX do not store users’ funds on the exchange, but instead facilitate peer-to-peer cryptocurrency trading.

